|
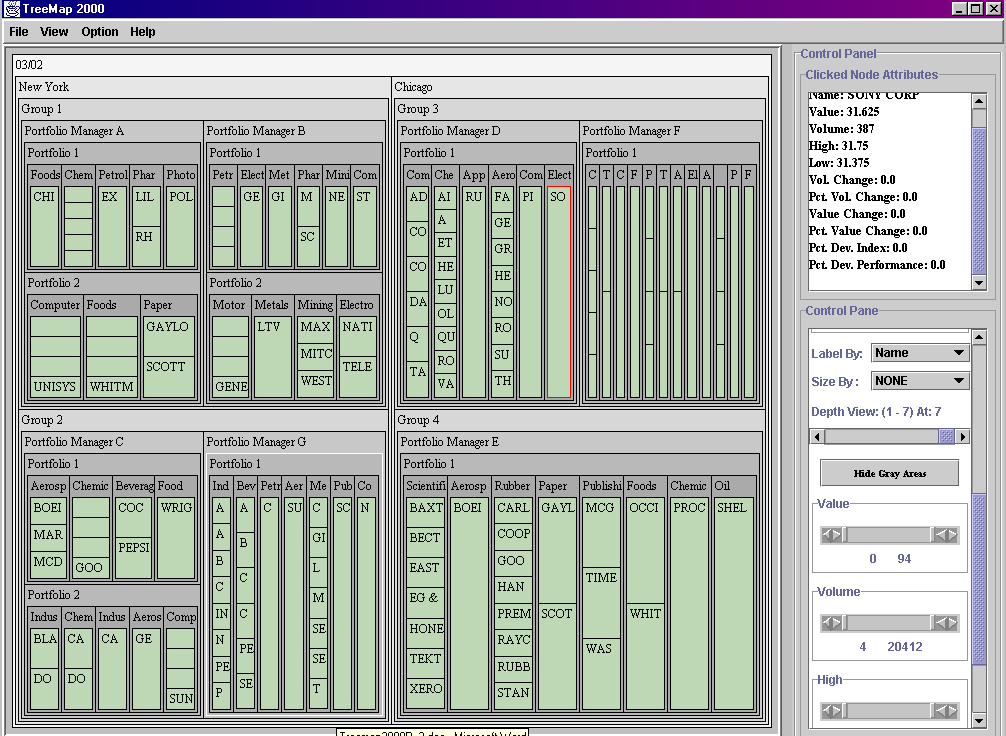
Treemap2000 is developed by Raghuveera
N Chalasani, under the guidance and support of Dr.Ben
Shneiderman. Its a 100% Java application developed
using Java Swing components and widgets of HCIL.
Design Issues
Design issues that occurred during the development
of Treemap 2000 can be broadly classified into performance
and graphical related. Performance related issues come
into play during the process of making dynamic queries
and during repainting the display area. There is a need
for speed and unfortunately the size of the data set,
as usual, hinders performance. The data structure was
carefully chosen and was augmented with various kinds
of internal structures improve better performance. Due
to the implementation of dynamic queries, a linked list
of double sliders is maintained for various kinds of
query processing.
Graphical issues include choosing the colors and implementing
double sliders for certain functions. Colors were poorly
implemented in Treemap 97. There was only one selection
of continuous colors and choosing discrete colors was
open to all kinds of data types. The version of Treemap
2000 has a better implementation of colors. The leaf
nodes are given a color based upon the data types. That
is, if the data type is either an integer or a float
than a continuous color shade is given to each leaf
node. There is also a selection of continuous colors:
red, blue and green. The gives the user a better view
of data based upon his or her choice.
The discrete coloring on the other hand is given only
to data types that are of type string and date. This
was implemented due to the lack of implementation of
alpha sliders. The string and date type attributes are
each assigned a particular color based upon their value.
If there are more than nine values, a number that represents
the number of discrete colors displayed, then the remaining
values of that type are given the same color.
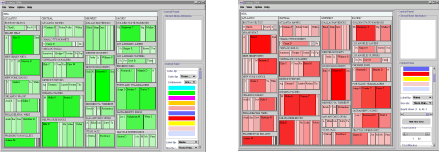
Another new coloring feature that is added to Treemap 2000 is the darkening
of internal nodes as depth increases to show the depth
feature of the Treemap. This feature takes display of
internal nodes to a new height. It allows a better usage
of display area by giving variable depth colors, instead
of giving a standard color to all the internal nodes.
Dynamic Queries functionality is another relevant design
issue encountered during the process of design. There
are three major steps in implementation of dynamic queries
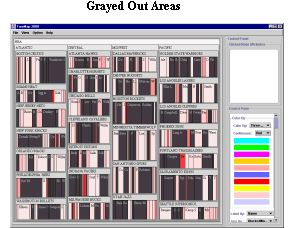
in Treemap 2000. The first step is the Graying Out.
This step is basically involves graying out areas that
are in the gray region of the double sliders. The second
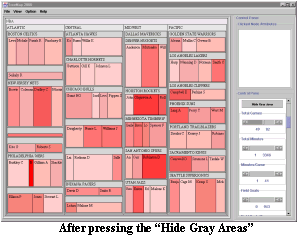
step is hiding gray areas and this step is accomplished
by pressing the "Hide Grayed Areas" button. After pressing
the button, all the grayed out areas are hidden and
the non-grayed out areas take over the display areas
of the grayed out areas. The way this function was implemented,
it will allow a particular internal node to be hidden
in case if all its leaf nodes are hidden. The final
step in dynamic queries is redrawing the hidden areas
upon the resetting of the sliders to the original position.
Decisions Made
Certain decisions (will be discussed in appendix) about
the architecture were made to increase the performance
of Treemap 2000 and to facilitate dynamic queries. Depth
incremental coloring was made to provide a better view
of Treemaps and for efficient usage of the space provided
for display. This type of coloring gives users a better
understanding about the structure and grouping of various
nodes.
The coloring clearing represents grouping of siblings
and distinguishes children from their parents. A choice
of continuous colors was given in order for the user
to have a view of their liking and to provide more flexibility
over coloring. Discrete colors are assigned to Treemaps
with less than 10 nodes regardless of the type of the
attribute chosen.
Future of Treemaps
There is an ample amount of possible areas of development
to Treemaps 2000. Adding Alpha and Date sliders for
Dynamic Querying is one of them.
Due to the time constraint, this functionality wasn't
implemented and is open for further exploration. Another
area for further exploration is discrete coloring. Assigning
distinct colors for all the different values that are
available for a chosen data type. A choice of both continuous
and distant colors for string and date types is definitely
something that should be done. Also, user customization
of colors can be implemented for discrete coloring.
A possible and interesting idea to explore is a choice
of different types of algorithms during redisplay. For
example, the user should be able to draw a particular
data set with Top-Down, Slide-and-Dice, and Squaring
algorithms.
Download
Treemap2000 has been developed on Windows NT 4.0 using
Java 1.2.2. It requires packages of HCIL and can only
be used for educational purposes. Others, please look
at the contact for further details. But I have been
sucessfully ran it on Windows 98 and Windows 2000 using
Java 1.2.2. I have never tried to run it on UNIX or
LINUX. But I donot see any reason why it wouldn't run.
Please try it if you want to and email me about any
problems encountered.
For licensing info for Treemap2000, please contact
Gayatri Varma of the UMD Office of Technology Commercialization.
|

